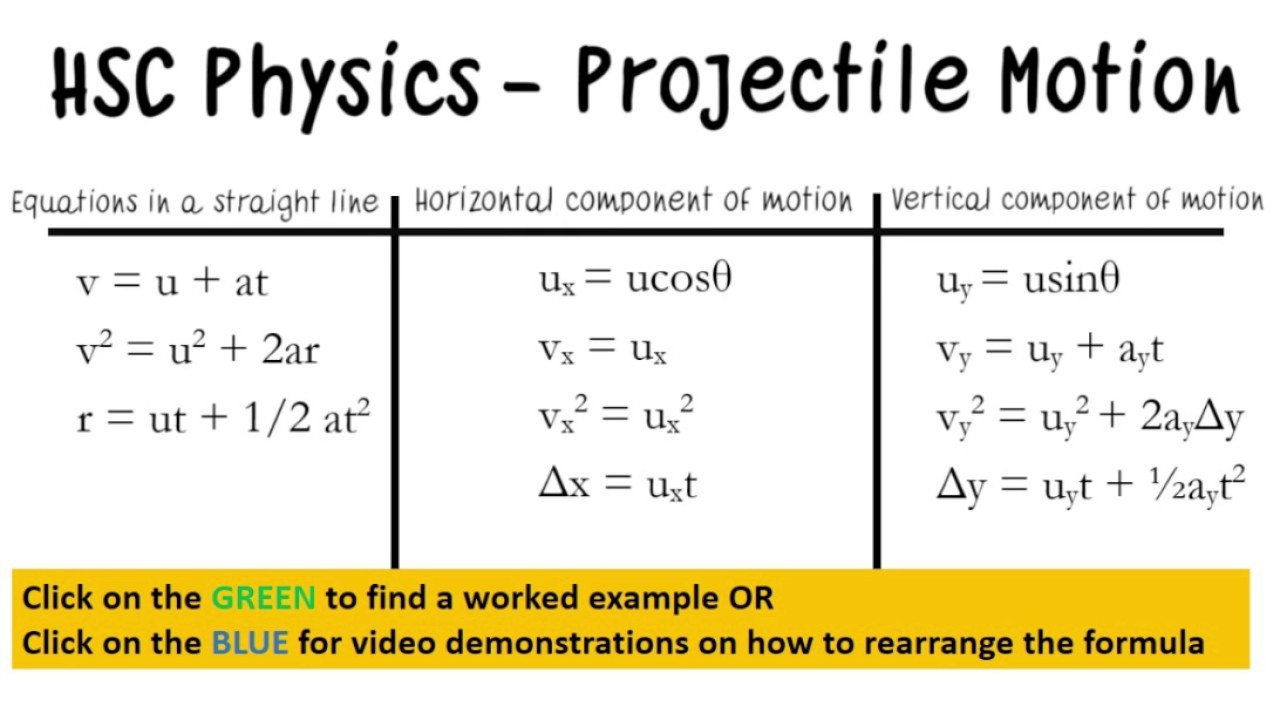
Projectile Motion
This animation shows the parabolic path of a ball rolled off of something like a table and then allowed to fall freely. Click play to set it in motion. The projectile is the magenta ball; the green balls represent its horizontal and vertical velocities.Notice that the horizontal velocity is constant, while the downward motion is accelerated. Run the animation a few times looking at different aspects of the motion. Look at both the forward progress (top) and the downward progress (left) of the ball.The essence of how we treat projectile motion, the motion of a launched object after no more launching forces are working on it, is in this figure: The horizontal velocity (ignoring friction) is constant, and the vertical acceleration is just that of a freely-falling object. A projectile is any object set free of any forces except for gravity and friction. A projectile can be a thrown ball, a bullet or a springboard diver.Except for air resistance, the forward velocity of any projectile is constant and is equal to the initial velocity when it was released.
The vertical velocity changes by the acceleration of gravity.Nature doesn't care that a projectile is moving forward. It's downward acceleration is just the acceleration of gravity, exactly as though it was dropped or thrown straight upward. Consider the forces at work on a ball while it's rolling along the table. We assume that a force was or is being applied that created a constant velocity v x. The force of gravity, F g, on the ball is exactly balanced by the normal force, F N, of the table pushing back on the ball.Now as the ball rolls off the table, the normal force vanishes and the force of gravity pulls it downward.
Projectile Motion - PhET Interactive Simulations.
Unbalanced forces produce acceleration, so the ball will accelerate downward at 9.8 m/s 2. There is no force acting horizontally (except for friction – air resistance), so the forward velocity will remain v x.
As the ball falls, two things are going on independently. First, the ball is traveling forward at a constant velocity. You can see that by the even spacing of the tick marks along the horizontal axis in the figure below.As time unfolds, the downward velocity of the ball increases at the rate of 9.8 m/s 2, creating the uneven spacing in the vertical location of the ball (ticks on vertical axis).That's the essence of projectile motion, no matter how complicated the scenario: Nature doesn't care about whether a projectile is moving horizontally. It's still going to be acted on by the force of gravity just as though it were dropped or thrown straight upward. Solution: Here's a picture of the situation. The ball is hit upward at a 45˚ angle with the ground, but gravity takes over immediately, bending the path into the downward parabola shown. For this problem we'll assume the distance from the bat to the ground is too small to matter.We'll need to break that initial velocity vector into its vertical and horizontal components to get the vertical velocity, vy and the horizontal velocity v x.
Vagrant Queen is an American sci-fi television series that premiered on Syfy on March 27, 2020. The series is based on the Vault comic book series written by Magdalene Visaggio and illustrated by Jason Smith. Elida built a life as a scavenger and outlaw, but when an old frenemy, Isaac, turns up with news about her long-lost mother, she. A former queen must travel across the galaxy to rescue her mother before a dangerous foe finds her. Watch full episodes of Vagrant Queen on SYFY. Watch full episodes of Vagrant Queen and get the latest breaking news, exclusive videos and pictures, episode recaps and much more at TVGuide.com. Vagrant queen wiki. Created by Jem Garrard. With Adriyan Rae, Alex McGregor, Paul du Toit, Colin Moss. This follows Elida from child queen to orphaned outcast, as she scavenges the treacherous corners of the galaxy, always one step ahead of the Republic government out to extinguish her bloodline. When her old friend Isaac shows up claiming her mother Xevelyn is still alive, they head off with their new ally, Amae. Vagrant Queen is filled with poorly written dialogue, cheesy fight scenes, very fake props, and overacting. Throwbacks to classic science fiction scenes are too obvious to be cute.
To do that we can use the 45-45-90 triangle, which you should memorize.The length of a side of the 45-45-90 triangle is √2/2 times the length of the hypotenuse, so our hitter diagram looks like this. Solution: In this problem we'll examine the effect of launch angle on the range (distance traveled) by a projectile. Here's the picture:The question we're really asking here is, which angle is the best for achieving the largest distance of the shot? We'll guess that it's 45˚ and test an angle on either side, 40˚ and 50˚.This problem will require a little trigonometry because not all of those angles belong to convenient memorized triangles.
The vertical ( v y) and horizontal ( v x) components of the muzzle velocity (that's just armament talk for the velocity of the cannonball or bullet as it exits the barrel) are shown here:Let's calculate those vector components of the velocity for each angle using the sines and cosines. Now we need to calculate the total time in the air using the definition of acceleration and the fact that the vertical velocity at the top of the arc is zero. The factor of 2 in this equation accounts for the round-trip up and back down.Here are the results for each angle:Now to calculate the distances using the horizontal velocities and the time interval,Finally, here are the distances:Indeed, the 45˚ angle yields the greatest distance. This is always true for a given initial velocity, all other conditions being equal. Practice problems 1.A ball is launched straight upward with an initial velocity of 3.0 m/s. The point where the ball exits from the mechanical launcher is 0.25 m from the ground.
How high above the ground will the ball go?Solution2.If a ball shot vertically rises to a height of 2.35 meters, what was its initial velocity?Solution3.A ball rolls toward the edge of a 37 m tall vertical cliff at a velocity of 5 m/s. Calculate how far the ball will be from the cliff when it hits the ground.Solution4.A suitcase was dropped from a plane traveling at 300 m/s at an altitude of 35,000 ft. Calculate the horizontal distance, between the point where the suitcase was dropped and the point where it landed.
Assume that there is no air resistance. (1m = 3.28 ft.)Solution5.A rifle with a muzzle velocity of 829 m/s is fired at a 32˚ angle with respect to the ground. Ignoring air resistance, how far away would the bullet land. Assume the bullet is fired from ground level. Does your answer make sense?Solution6.Consider the case of a shot putter throwing a 9 lb.
Shot put in a competition. To achieve optimum distance, the thrower hurls the steel ball at a 45˚ upward angle. He can generate enough acceleration of the shot to achieve an initial velocity of 14.1 m/s. How far will the shot put fly? Assume that the release point is 8 ft. Off the ground and that the ball lands on level ground.
The world record in the men's shot put event is 23.12 mSolution.